2 月 . 10, 2025 12:32 Back to list
Tempered Glass
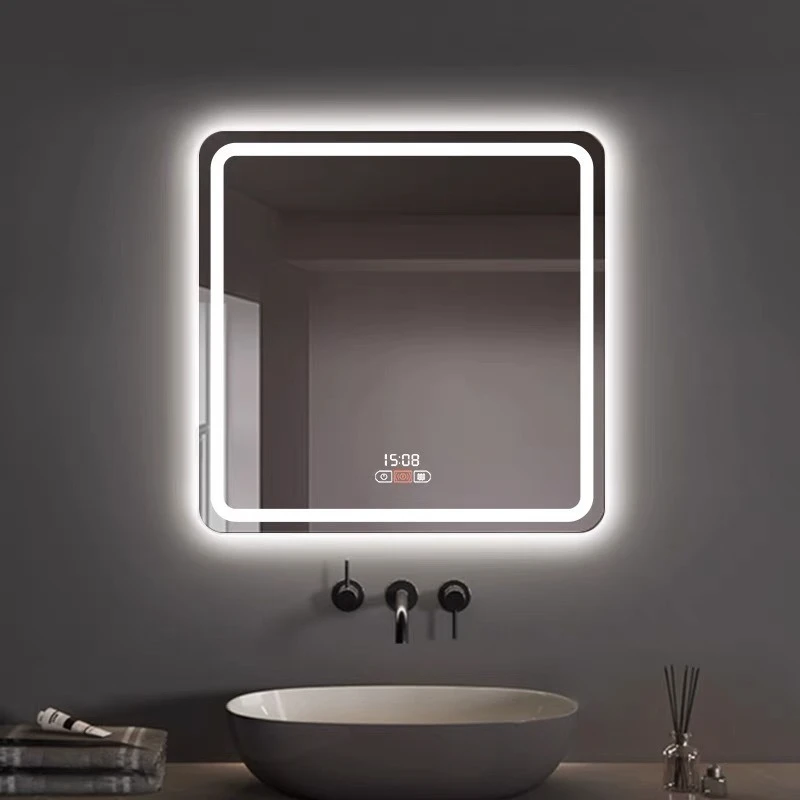
Tempered laminated glass stands as a key innovation in the realm of safety and architectural applications. This specific type of glass merges the strengths of two distinctive glass types—tempered glass and laminated glass—each contributing unique qualities to the final product. Understanding the nature, creation, and applications of tempered laminated glass illuminates its importance in modern construction and design, as well as the reasons it has become a preferred material in numerous industries.
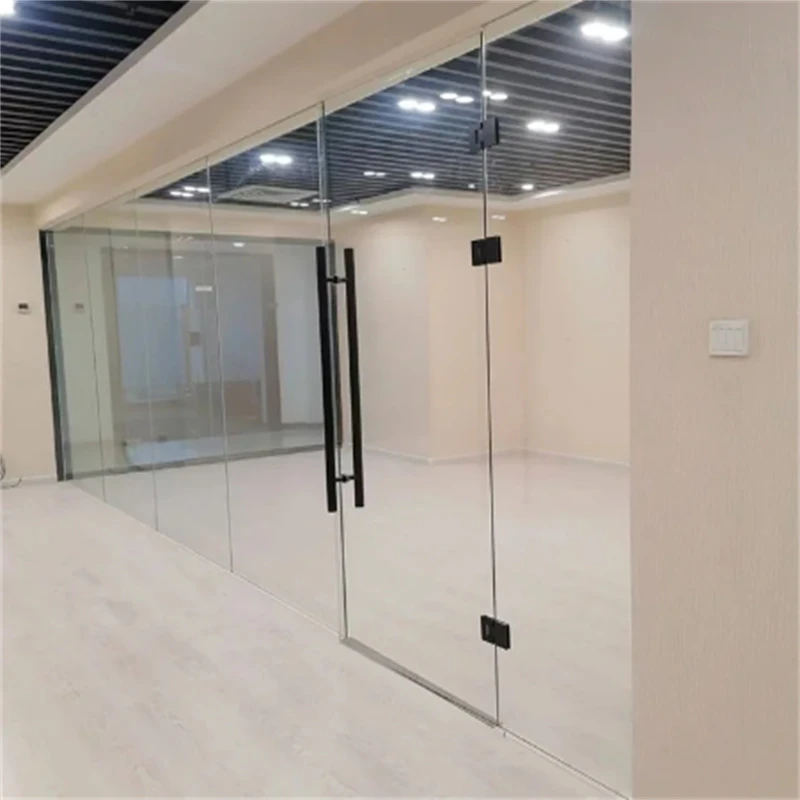
Beyond the practicalities of safety and soundproofing, tempered laminated glass also provides considerable energy efficiency benefits. It assists in regulating temperature by blocking significant portions of ultraviolet (UV) rays and infrared radiation, which can reduce heating and cooling costs. The interlayer in the glass filters these types of radiation without compromising light transmission, making it a sustainable option for energy-conscious consumers and builders. Architecturally, tempered laminated glass offers extensive versatility in design. It supports greater spans and unique shapes, which architects can employ to create innovative and aesthetic structures. The thickness and color of the laminate can be customized without sacrificing the material's inherent strength. Buildings benefit not only from the functional attributes of the glass but also from its ability to enhance visual appeal, providing both transparency and security. Moreover, the environmental impact of tempered laminated glass contributes to its desirability. PVB interlayers often come from recycled materials, increasing its sustainability quotient. Its long lifespan reduces the frequency of replacements, aiding in the conservation of resources and lowering greenhouse effects associated with manufacturing processes. Tempered laminated glass embodies a synergy of modern engineering and design, offering unrivaled benefits that cater to contemporary architectural demands for safety, efficiency, and aesthetics. Its usage demonstrates advances in material science that meet diverse needs, from enhancing security to increasing energy efficiency and even contributing to ecological sustainability. Consequently, for those immersed in the fields of architecture, construction, and innovative design, tempered laminated glass is not merely an option but an irreplaceable resource that fulfills multiple industry standards and enhances the quality of life while ensuring safety and durability.


Beyond the practicalities of safety and soundproofing, tempered laminated glass also provides considerable energy efficiency benefits. It assists in regulating temperature by blocking significant portions of ultraviolet (UV) rays and infrared radiation, which can reduce heating and cooling costs. The interlayer in the glass filters these types of radiation without compromising light transmission, making it a sustainable option for energy-conscious consumers and builders. Architecturally, tempered laminated glass offers extensive versatility in design. It supports greater spans and unique shapes, which architects can employ to create innovative and aesthetic structures. The thickness and color of the laminate can be customized without sacrificing the material's inherent strength. Buildings benefit not only from the functional attributes of the glass but also from its ability to enhance visual appeal, providing both transparency and security. Moreover, the environmental impact of tempered laminated glass contributes to its desirability. PVB interlayers often come from recycled materials, increasing its sustainability quotient. Its long lifespan reduces the frequency of replacements, aiding in the conservation of resources and lowering greenhouse effects associated with manufacturing processes. Tempered laminated glass embodies a synergy of modern engineering and design, offering unrivaled benefits that cater to contemporary architectural demands for safety, efficiency, and aesthetics. Its usage demonstrates advances in material science that meet diverse needs, from enhancing security to increasing energy efficiency and even contributing to ecological sustainability. Consequently, for those immersed in the fields of architecture, construction, and innovative design, tempered laminated glass is not merely an option but an irreplaceable resource that fulfills multiple industry standards and enhances the quality of life while ensuring safety and durability.
Next:
Latest news
-
Wired Glass: A Strong and Secure Glass Solution for Various Applications
NewsNov.04,2024
-
Tinted Glass: A Stylish and Functional Choice for Modern Homes
NewsNov.04,2024
-
The Elegance and Versatility of Silver Mirrors
NewsNov.04,2024
-
The Advantages of Copper Free Mirrors
NewsNov.04,2024
-
Tempered Glass: A Reliable Choice for Modern Applications
NewsNov.04,2024
-
Pattern Glass: Stylish and Functional Glass for Modern Design
NewsNov.04,2024
Related PRODUCTS