1 月 . 19, 2025 05:06 Back to list
Float Glass
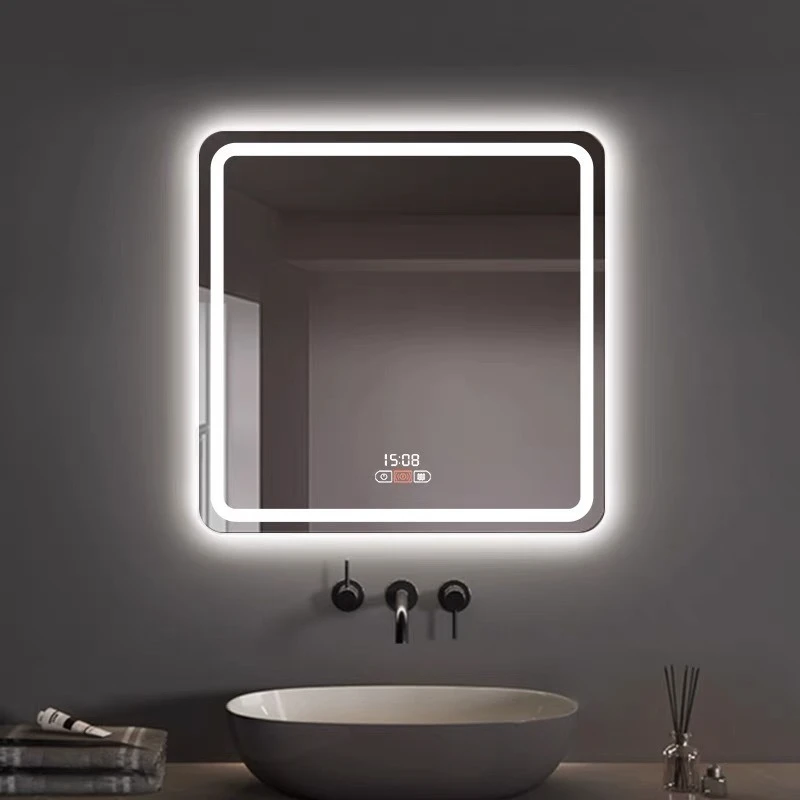
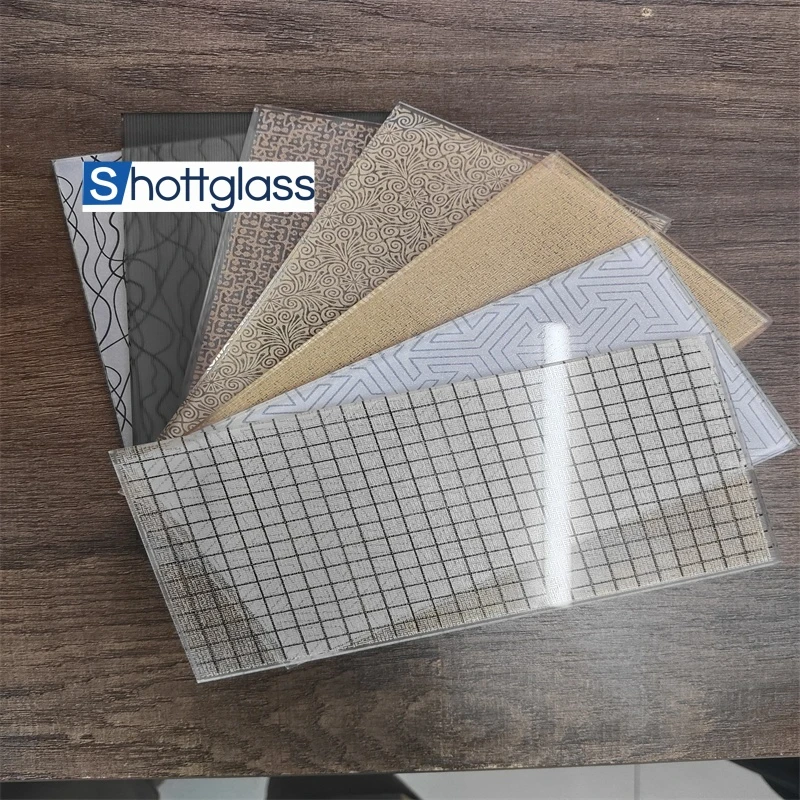
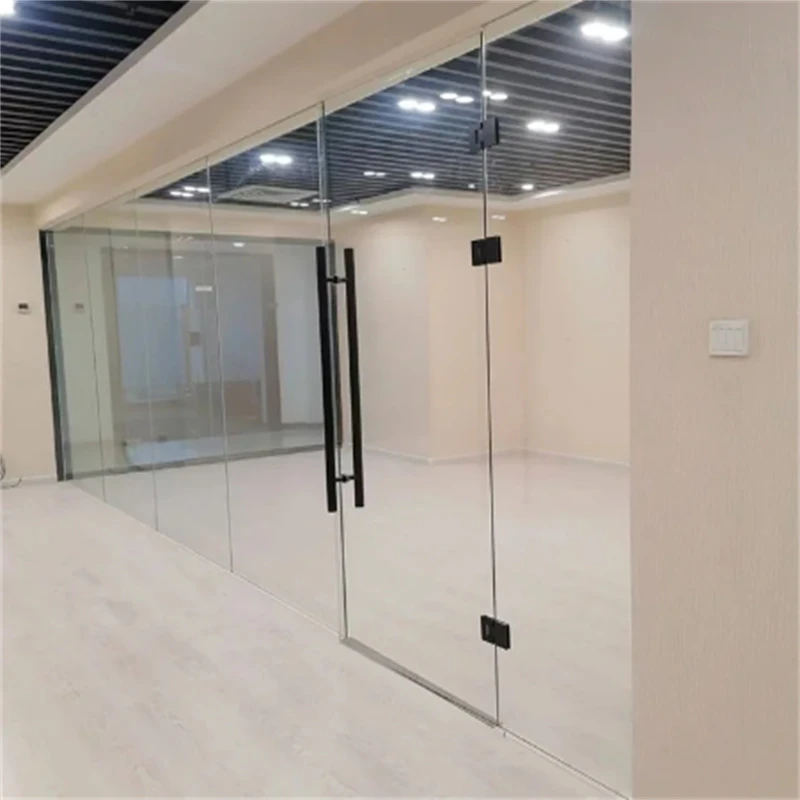
Float glass is one of the most versatile and widely used materials in construction and manufacturing today, offering a perfect blend of optical clarity and mechanical strength. Its production process, which involves floating molten glass on a bed of molten tin, results in a high-quality sheet of glass with uniform thickness and exceptional flatness. This innovative method, developed in the mid-20th century, revolutionized the glassmaking industry, making float glass an indispensable component in numerous applications.
Science and technology fields also harness the unique properties of float glass, especially in the production of high-precision scientific instruments and electronics. Its flatness and uniformity are essential in the manufacturing of liquid crystal displays (LCDs), photovoltaic panels, and touchscreen devices. The demand for thinner, yet stronger glass in these tech applications continues to drive innovations in float glass manufacturing. Sustainability is another aspect where float glass shines; it's 100% recyclable without loss of quality. The industry has committed to reducing its environmental footprint through efficient production techniques and recycling initiatives. This commitment not only conserves resources but also aligns with the growing global emphasis on sustainable development. In recent years, smart glass technology has emerged, using float glass as its foundation. Smart glass can change its light transmission properties when voltage, light, or heat is applied, making it ideal for energy-smart buildings that regulate their heat intake and lighting needs autonomously. In summary, the uses of float glass extend well beyond conventional applications, showcasing its adaptability and indispensability across various industries. From its fundamental role in building and automotive sectors to its contributions in cutting-edge technology and sustainable practices, float glass stands as a testament to the innovative spirit of modern manufacturing. Its ongoing development promises to unlock even more potential uses, reinforcing its status as a cornerstone material in both current and future design and engineering endeavors.


Science and technology fields also harness the unique properties of float glass, especially in the production of high-precision scientific instruments and electronics. Its flatness and uniformity are essential in the manufacturing of liquid crystal displays (LCDs), photovoltaic panels, and touchscreen devices. The demand for thinner, yet stronger glass in these tech applications continues to drive innovations in float glass manufacturing. Sustainability is another aspect where float glass shines; it's 100% recyclable without loss of quality. The industry has committed to reducing its environmental footprint through efficient production techniques and recycling initiatives. This commitment not only conserves resources but also aligns with the growing global emphasis on sustainable development. In recent years, smart glass technology has emerged, using float glass as its foundation. Smart glass can change its light transmission properties when voltage, light, or heat is applied, making it ideal for energy-smart buildings that regulate their heat intake and lighting needs autonomously. In summary, the uses of float glass extend well beyond conventional applications, showcasing its adaptability and indispensability across various industries. From its fundamental role in building and automotive sectors to its contributions in cutting-edge technology and sustainable practices, float glass stands as a testament to the innovative spirit of modern manufacturing. Its ongoing development promises to unlock even more potential uses, reinforcing its status as a cornerstone material in both current and future design and engineering endeavors.
Next:
Latest news
-
Wired Glass: A Strong and Secure Glass Solution for Various Applications
NewsNov.04,2024
-
Tinted Glass: A Stylish and Functional Choice for Modern Homes
NewsNov.04,2024
-
The Elegance and Versatility of Silver Mirrors
NewsNov.04,2024
-
The Advantages of Copper Free Mirrors
NewsNov.04,2024
-
Tempered Glass: A Reliable Choice for Modern Applications
NewsNov.04,2024
-
Pattern Glass: Stylish and Functional Glass for Modern Design
NewsNov.04,2024
Related PRODUCTS