10 月 . 14, 2024 02:25 Back to list
toughened glass and laminated glass
Toughened Glass and Laminated Glass A Comprehensive Overview
When it comes to modern architecture and design, the choice of materials plays a crucial role in ensuring safety, functionality, and aesthetics. Among the various options available in the market, toughened glass and laminated glass stand out as two of the most popular choices due to their remarkable properties and wide applications. In this article, we will explore the characteristics, manufacturing processes, advantages, and typical uses of toughened glass and laminated glass, highlighting the reasons behind their growing prominence.
What is Toughened Glass?
Toughened glass, also known as tempered glass, is a type of safety glass that has been processed to increase its strength compared to normal glass. The manufacturing process involves heating the glass to a temperature of around 620-650 degrees Celsius and then rapidly cooling it. This thermal treatment creates a balanced internal stress in the glass, making it much more resistant to impacts and thermal fluctuations.
One of the most significant advantages of toughened glass is its safety features. In the event of breakage, toughened glass shatters into small, blunt pieces rather than sharp shards, significantly reducing the risk of injury. This characteristic makes it an ideal choice for various applications, including shower doors, glass doors and tables, facades, and windows in high-rise buildings.
What is Laminated Glass?
Laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass held together by a layer of interlayer material, typically made from polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA). The process involves placing the interlayer between the layers of glass and applying heat and pressure to bond them. This results in a composite material that not only maintains the transparency and aesthetic appeal of the glass but also enhances its safety and performance.
Laminated glass is well-known for its excellent sound insulation and UV protection properties. The interlayer effectively absorbs sound waves, making it a popular choice for buildings located in noisy environments. Additionally, it blocks up to 99% of harmful UV rays, protecting both the interiors and occupants from potential harm.
Advantages of Toughened and Laminated Glass
Both toughened and laminated glass offer unique benefits that cater to various needs
1. Safety and Security Toughened glass's ability to shatter into harmless pieces and laminated glass's resistance to breakage make both options safer than regular glass. Laminated glass remains intact even when broken, providing an additional layer of security against forced entry.
toughened glass and laminated glass

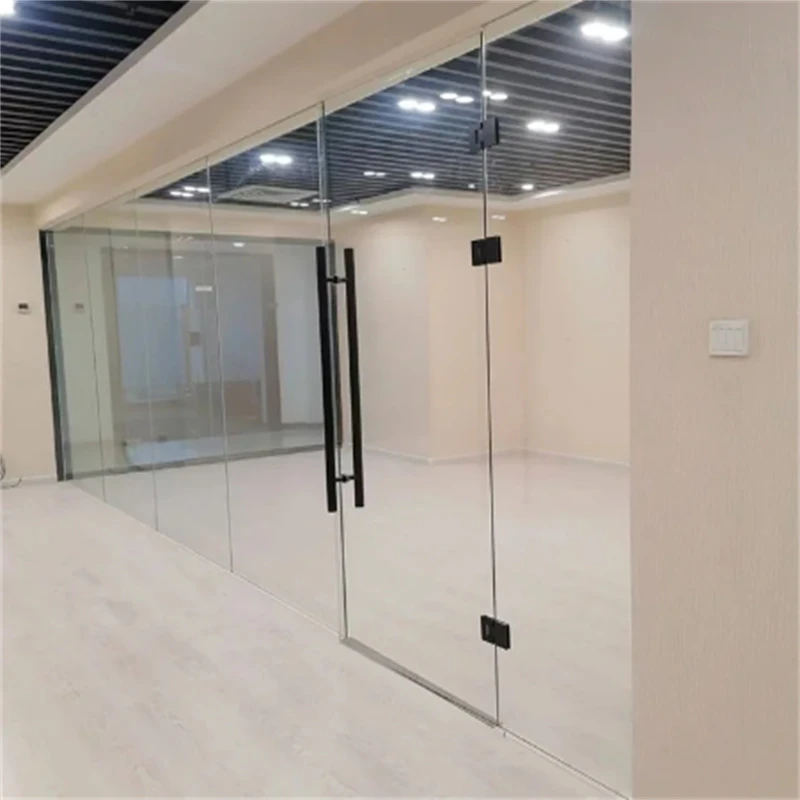
2. Durability Toughened glass is highly durable and can withstand larger impacts and temperature variations than ordinary glass. Laminated glass also offers durability, particularly in areas that require additional structural support.
3. Versatility Both types of glass can be used in various applications. Toughened glass is commonly used in facades, glass balustrades, and partition walls, while laminated glass is often employed in overhead glazing, skylights, and acoustic panels.
4. Aesthetic Appeal Both forms of glass can enhance the beauty of a structure. They are available in different finishes and colors, allowing architects and designers to create stunning visual effects.
Applications
Toughened and laminated glass are utilized in numerous applications across different sectors
- Residential Buildings Toughened glass is frequently used in shower enclosures, glass doors, and windows. Laminated glass is an excellent choice for skylights and balcony railings, as it enhances safety without compromising on style.
- Commercial Buildings In commercial settings, toughened glass is used for storefronts, partitions, and atriums, whereas laminated glass is often chosen for conference rooms and offices requiring soundproofing.
- Automotive Industry Laminated glass is widely used in car windshields due to its strength and safety features, providing protection during accidents and contributing to passenger safety.
Conclusion
In conclusion, toughened glass and laminated glass are two essential materials in contemporary design and construction. Their unique properties offer numerous advantages, including safety, durability, and aesthetic flexibility. As technology advances and the demand for resilient and secure building materials continues to grow, both toughened and laminated glass are likely to remain at the forefront of architectural innovation. By understanding the benefits and applications of these materials, architects and builders can make informed decisions that enhance the safety and beauty of their projects, ultimately contributing to a more sustainable and stylish built environment.
-
Wired Glass: A Strong and Secure Glass Solution for Various Applications
NewsNov.04,2024
-
Tinted Glass: A Stylish and Functional Choice for Modern Homes
NewsNov.04,2024
-
The Elegance and Versatility of Silver Mirrors
NewsNov.04,2024
-
The Advantages of Copper Free Mirrors
NewsNov.04,2024
-
Tempered Glass: A Reliable Choice for Modern Applications
NewsNov.04,2024
-
Pattern Glass: Stylish and Functional Glass for Modern Design
NewsNov.04,2024
Related PRODUCTS