11 月 . 04, 2024 10:55 Back to list
Understanding the Differences Between Toughened Glass and Laminated Glass in Modern Architecture
Toughened Glass and Laminated Glass A Comparative Overview
In the modern architectural and construction landscape, glass plays a vital role not only as a functional element but also as an aesthetic one. Among the various types of glass commonly used, toughened (or tempered) glass and laminated glass stand out due to their unique properties and applications. Understanding the distinctions, advantages, and applications of these two types of glass is essential for professionals in construction, interior design, and safety engineering.
Toughened Glass Explained
Toughened glass is a type of glass that has been thermally treated to enhance its strength compared to standard glass. The manufacturing process involves heating the glass to a temperature of approximately 600°C and then rapidly cooling it. This process creates a compressive stress layer on the surface of the glass, which increases its resistance to impact and thermal stress.
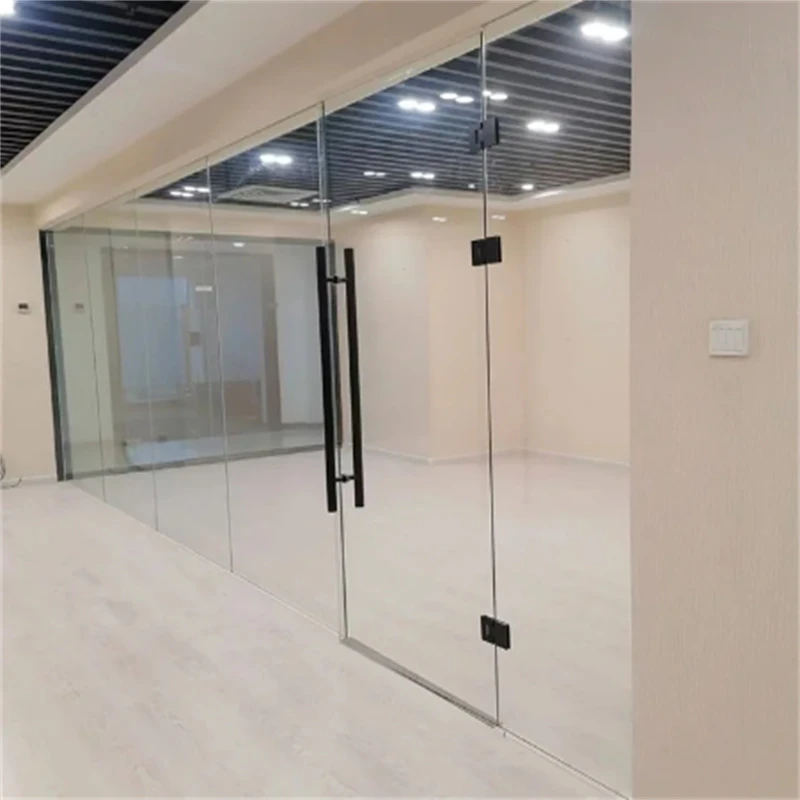
One of the most significant advantages of toughened glass is its strength. It is several times stronger than regular glass, making it an ideal choice for a variety of applications where safety and durability are priorities. In the event of breaking, toughened glass shatters into small, blunt pieces, reducing the risk of injury. Thus, it is commonly employed in environments such as car windows, shower doors, glass doors and tables, and facades of buildings.
Laminated Glass Overview
Laminated glass, on the other hand, consists of two or more layers of glass bonded together with a plastic interlayer, typically polyvinyl butyral (PVB). This interlayer not only enhances the glass's strength but also provides additional benefits, such as sound insulation and UV filtering. The laminated glass is processed by heating and pressing the layers together, creating a cohesive unit that retains its structure even when broken.
The primary advantage of laminated glass is its safety features. When broken, the glass remains adhered to the interlayer, minimizing the risk of shards falling and causing injury. This property makes laminated glass an ideal choice for applications requiring high safety standards, such as skylights, glass floors, and storefronts. Additionally, its ability to block UV radiation and reduce noise pollution makes it increasingly popular in residential and commercial buildings.
toughened glass and laminated glass

Key Differences Between Toughened and Laminated Glass
While both toughened and laminated glass offer enhanced safety compared to standard glass, their characteristics and use cases differ significantly
.1. Manufacturing Process Toughened glass undergoes a thermal tempering process, while laminated glass is created through the application of an interlayer between glass sheets.
2. Strength and Safety Toughened glass is designed to withstand high impacts and thermal stress, making it incredibly strong. Laminated glass, while not as strong as toughened glass in terms of impact resistance, offers superior safety features since the shards remain attached to the PVB interlayer after breaking.
3. Applications Toughened glass is often used in situations where high strength is required, such as in overhead glazing, while laminated glass is preferred in applications emphasizing safety and sound insulation, like in automotive windscreens and safety barriers.
4. Cost and Installation Toughened glass can be more expensive due to its processing requirements, and care must be taken in installation to avoid damage. Laminated glass can also be costly, but its benefits, particularly in safety, often justify the price in critical applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both toughened glass and laminated glass serve essential roles in modern-day construction and design. The choice between the two primarily depends on the specific needs of a project, including safety, aesthetics, and structural requirements. While toughened glass excels in strength and thermal resistance, laminated glass offers unmatched safety and sound attenuation properties. By understanding the differences and applications of these glass types, engineers, architects, and designers can make informed decisions that contribute to the safety, durability, and beauty of their projects.
-
Wired Glass: A Strong and Secure Glass Solution for Various Applications
NewsNov.04,2024
-
Tinted Glass: A Stylish and Functional Choice for Modern Homes
NewsNov.04,2024
-
The Elegance and Versatility of Silver Mirrors
NewsNov.04,2024
-
The Advantages of Copper Free Mirrors
NewsNov.04,2024
-
Tempered Glass: A Reliable Choice for Modern Applications
NewsNov.04,2024
-
Pattern Glass: Stylish and Functional Glass for Modern Design
NewsNov.04,2024
Related PRODUCTS