10 月 . 31, 2024 04:28 Back to list
tempered laminated glass specification
Tempered Laminated Glass Specification An Overview
Tempered laminated glass is a prominent material in modern architecture and design, known for its strength, safety, and aesthetic appeal. This type of glass combines the features of tempered glass and laminated glass, providing enhanced durability and protection. Understanding the specifications and properties of tempered laminated glass is essential for architects, builders, and designers who aim to utilize it in their projects.
What is Tempered Laminated Glass?
Tempered laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass bound together by an interlayer—commonly made from polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA)—to create a composite material. The glass layers are first tempered, which involves heating the glass to high temperatures to increase its strength. After cooling, the tempered glass is laminated by sandwiching the interlayer between the glass layers and applying heat and pressure, resulting in a strong bond.
Key Specifications
1. Thickness The thickness of tempered laminated glass typically ranges from 6mm to 20mm or more, depending on the application. The standard is usually between 10mm and 12mm for most commercial uses, ensuring adequate strength and safety.
2. Strength One of the main advantages of tempered laminated glass is its enhanced strength. Tempered glass can withstand high impacts and thermal stress, making it less likely to shatter compared to regular glass. When it does break, it crumbles into small, blunt pieces that minimize the risk of injury.
3. Safety and Security The laminated aspect of the glass adds an extra layer of safety. In the event of a breakage, the interlayer holds the pieces of glass together, preventing them from falling and reducing the risk of injuries. This characteristic is especially beneficial in high-traffic areas or locations prone to vandalism.
tempered laminated glass specification
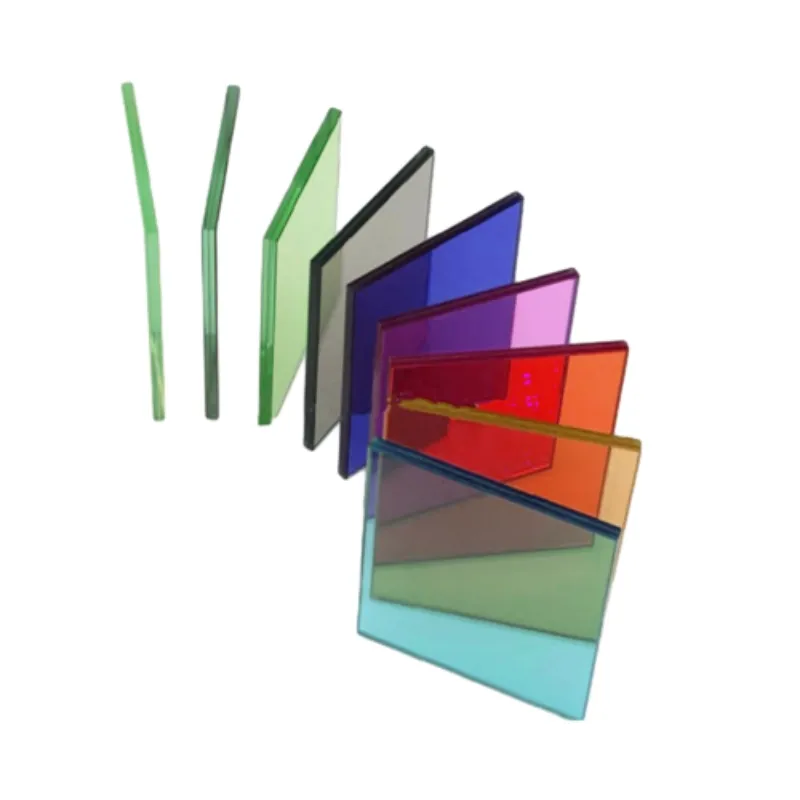
4. UV Protection Tempered laminated glass also offers protection against ultraviolet (UV) rays. The PVB interlayer can block up to 99% of harmful UV radiation, making it ideal for applications in which fade and damage to interior furnishings or artwork are concerns.
5. Acoustic Performance Another important specification is sound attenuation. The laminated construction effectively dampens sound transmission, making it an excellent choice for applications requiring acoustic insulation, such as offices, hotels, and residential buildings.
6. Thermal Performance Depending on the manufacturing process and materials used, tempered laminated glass can contribute to improved thermal insulation—a vital factor in energy-efficient designs. It can also help in controlling glare, thereby enhancing the overall comfort in a space.
Applications
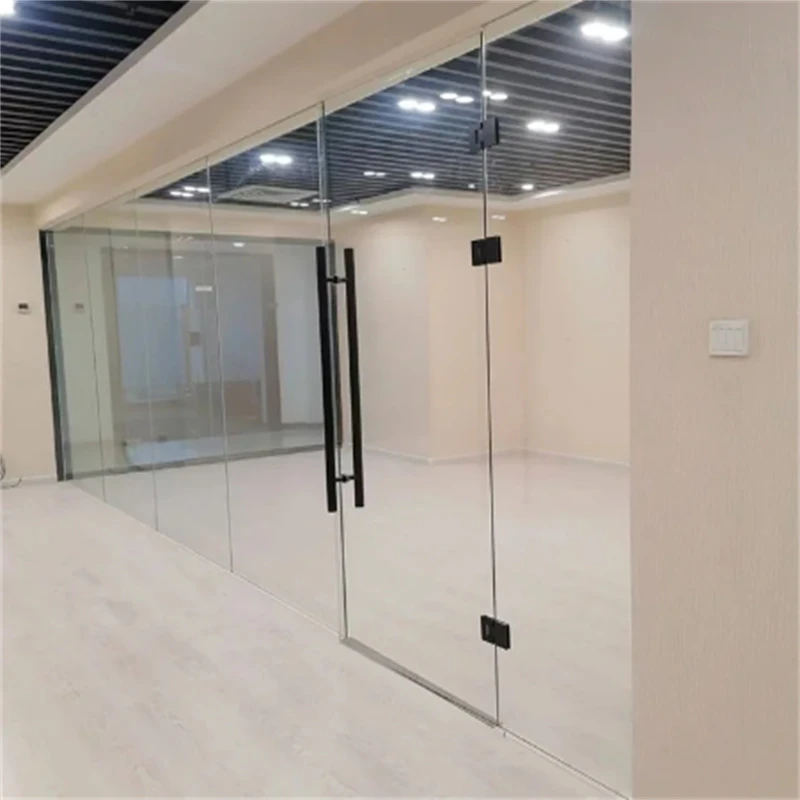
Due to its advantageous specifications, tempered laminated glass is widely used in various applications. Common uses include facades of commercial buildings, skylights, glass doors, and shower enclosures. It is also increasingly utilized in residential buildings for windows, balcony railings, and outer walls, where both safety and aesthetics are paramount.
Conclusion
Understanding the specifications of tempered laminated glass is crucial for making informed decisions in construction and design. Its exceptional strength, safety features, and aesthetic versatility make it a preferred choice in contemporary architecture. As advancements in technology continue to enhance its properties, tempered laminated glass will undoubtedly play a vital role in the future of building materials.
-
Wired Glass: A Strong and Secure Glass Solution for Various Applications
NewsNov.04,2024
-
Tinted Glass: A Stylish and Functional Choice for Modern Homes
NewsNov.04,2024
-
The Elegance and Versatility of Silver Mirrors
NewsNov.04,2024
-
The Advantages of Copper Free Mirrors
NewsNov.04,2024
-
Tempered Glass: A Reliable Choice for Modern Applications
NewsNov.04,2024
-
Pattern Glass: Stylish and Functional Glass for Modern Design
NewsNov.04,2024
Related PRODUCTS