1 月 . 15, 2025 09:21 Back to list
float glass sheets
Float glass sheets, renowned for their exceptional clarity and flatness, have revolutionized industries relying on high-quality glass. As we delve into the intricacies of this product, it’s crucial to consider the four pillars that enhance their market presence and usability real-world experience, expertise in production, authoritativeness in industry standards, and trustworthiness in application.
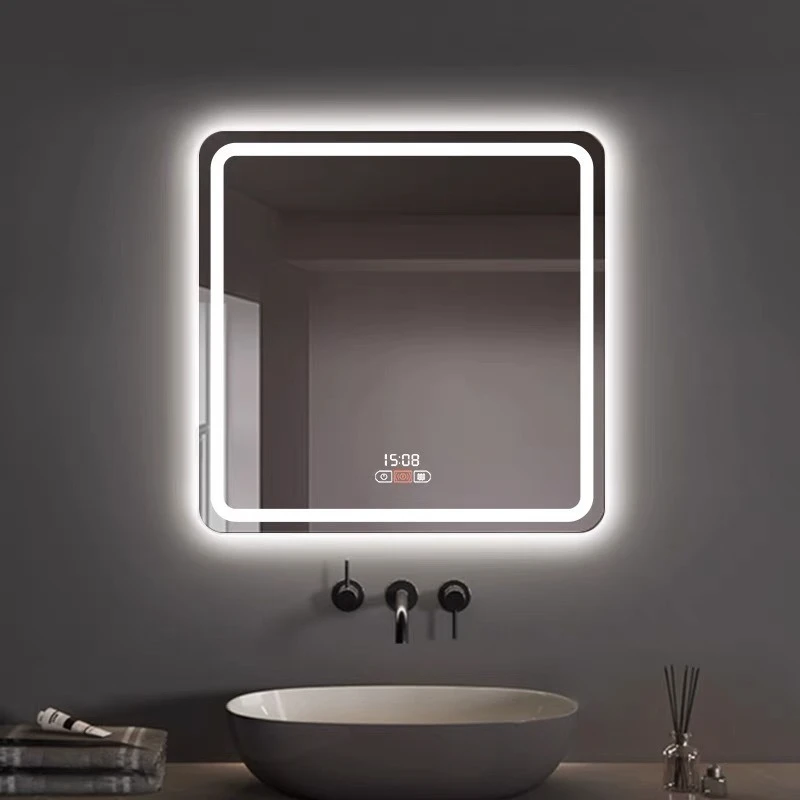
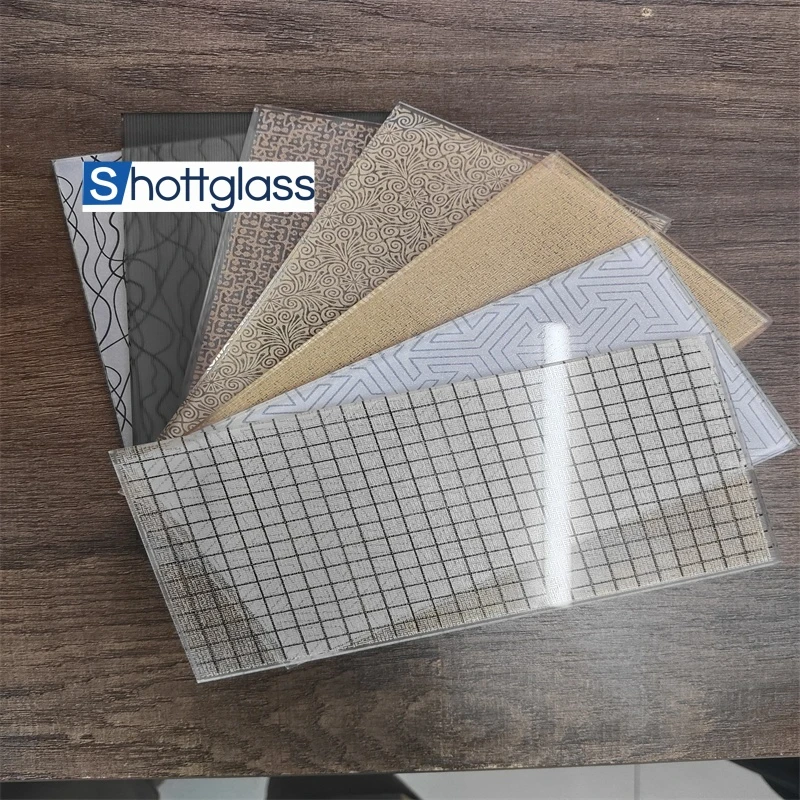
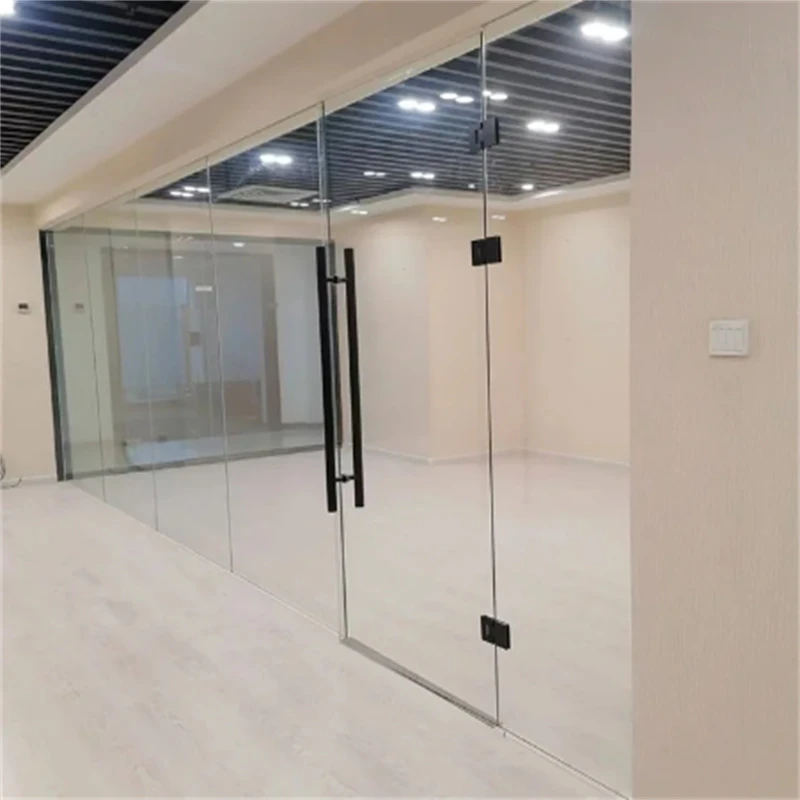
Real-world experience with float glass sheets often underscores their versatility. For example, in the interior design space, float glass is favored for partitions and flooring. Its ability to be cut into various shapes and sizes without compromising clarity makes it indispensable. Builders and designers speak highly of its adaptability and ease of installation, which streamline the construction process and reduce time on site. Moreover, float glass sheets play a critical role in the solar energy sector. As the quest for sustainable energy solutions intensifies, float glass’s exceptional transmittance properties make it an ideal candidate for solar panels. Its production can be fine-tuned to minimize iron content, enhancing its ability to conduct sunlight more efficiently than alternatives. The environmental implications of float glass production cannot be overlooked. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting environmentally friendly practices, minimizing carbon footprints during production. Innovations such as the use of recycled materials and reducing energy consumption during the manufacturing process are at the forefront, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers and aligning the industry with global sustainability goals. In conclusion, float glass sheets are emblematic of how expertise, consistent quality, adherence to standards, and proven reliability can elevate a product's status in various sectors. As architectural aesthetics continue to evolve, and industries demand materials that offer both performance and sustainability, float glass remains an unrivaled solution. Its multifaceted applications, coupled with ongoing innovations, ensure that it will remain integral to future design and construction paradigms.
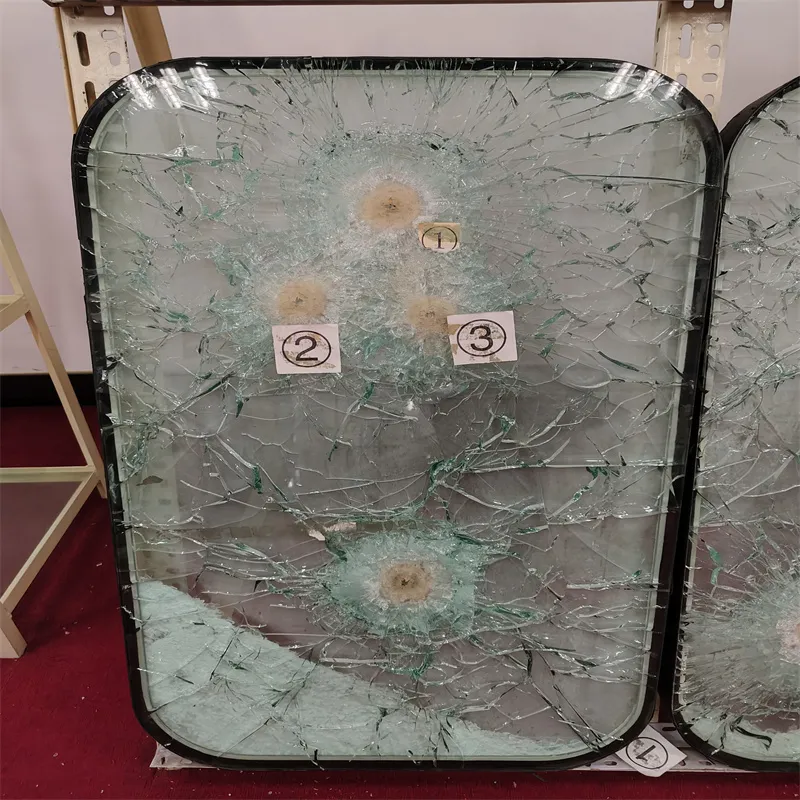


Real-world experience with float glass sheets often underscores their versatility. For example, in the interior design space, float glass is favored for partitions and flooring. Its ability to be cut into various shapes and sizes without compromising clarity makes it indispensable. Builders and designers speak highly of its adaptability and ease of installation, which streamline the construction process and reduce time on site. Moreover, float glass sheets play a critical role in the solar energy sector. As the quest for sustainable energy solutions intensifies, float glass’s exceptional transmittance properties make it an ideal candidate for solar panels. Its production can be fine-tuned to minimize iron content, enhancing its ability to conduct sunlight more efficiently than alternatives. The environmental implications of float glass production cannot be overlooked. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting environmentally friendly practices, minimizing carbon footprints during production. Innovations such as the use of recycled materials and reducing energy consumption during the manufacturing process are at the forefront, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers and aligning the industry with global sustainability goals. In conclusion, float glass sheets are emblematic of how expertise, consistent quality, adherence to standards, and proven reliability can elevate a product's status in various sectors. As architectural aesthetics continue to evolve, and industries demand materials that offer both performance and sustainability, float glass remains an unrivaled solution. Its multifaceted applications, coupled with ongoing innovations, ensure that it will remain integral to future design and construction paradigms.
Next:
Latest news
-
Wired Glass: A Strong and Secure Glass Solution for Various Applications
NewsNov.04,2024
-
Tinted Glass: A Stylish and Functional Choice for Modern Homes
NewsNov.04,2024
-
The Elegance and Versatility of Silver Mirrors
NewsNov.04,2024
-
The Advantages of Copper Free Mirrors
NewsNov.04,2024
-
Tempered Glass: A Reliable Choice for Modern Applications
NewsNov.04,2024
-
Pattern Glass: Stylish and Functional Glass for Modern Design
NewsNov.04,2024
Related PRODUCTS