1 月 . 19, 2025 03:36 Back to list
clear float glass price
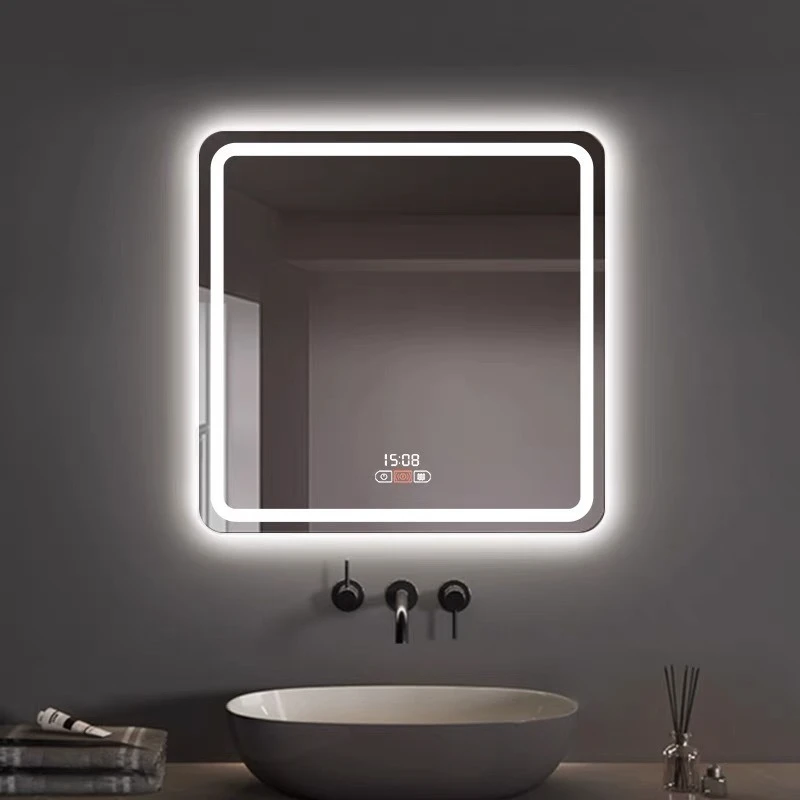
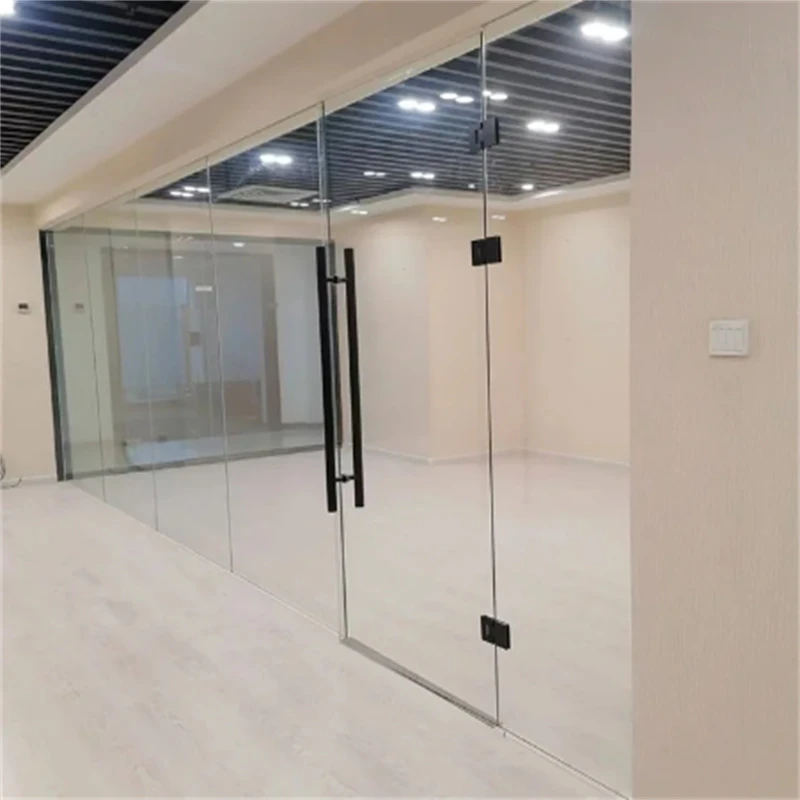
Float glass, a staple in modern construction and design, continues to pique the interest of consumers and industry professionals alike due to its versatile applications and cost implications. To understand the factors influencing float glass prices, one must delve into both market dynamics and production complexities.
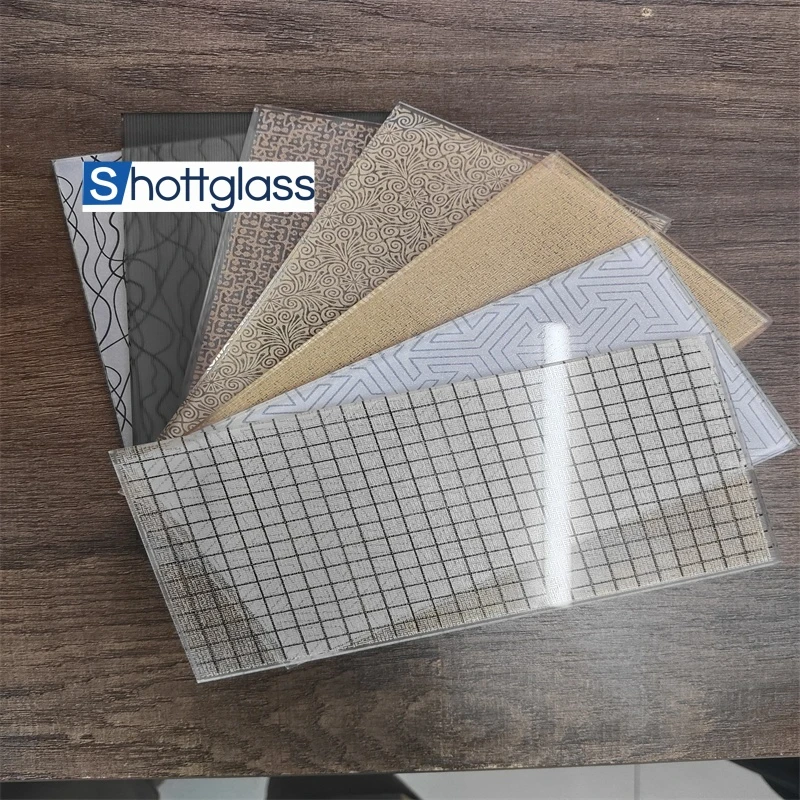
Moreover, expertise in crafting specialized float glass variants, such as tempered or coated glass, offers manufacturers a competitive edge, enabling them to cater to diverse applications ranging from energy-efficient windows to high-performance architectural facades. These specialized products often carry a premium price due to their enhanced properties and performance benefits, representing a significant portion of the float glass industry's value-added segment. An authoritative understanding of float glass pricing also involves recognizing environmental impacts. The industry faces increasing scrutiny over carbon emissions, prompting manufacturers to adopt sustainable practices. As eco-friendly production methods become prevalent, initial costs may rise; however, in the long-term, these practices offer cost savings through improved energy efficiency and resource management. Trust in float glass suppliers, therefore, hinges on their commitment to both innovation and sustainability, influencing purchasing decisions and pricing trends. Advisors recommend monitoring market publications and engaging in continuous dialogue with suppliers to navigate the intricate landscape of float glass pricing effectively. By investing in long-term partnerships and understanding supplier capabilities, buyers can secure favorable pricing while ensuring the quality and consistency of float glass products. In conclusion, the price trajectory of float glass is an intricate tapestry woven from production costs, market demand, regional influences, technological advancements, and environmental considerations. Navigating these factors requires a combination of experience, expertise, authority, and trustworthiness—qualities that professionals in the float glass market continually refine to understand and predict industry trends.


Moreover, expertise in crafting specialized float glass variants, such as tempered or coated glass, offers manufacturers a competitive edge, enabling them to cater to diverse applications ranging from energy-efficient windows to high-performance architectural facades. These specialized products often carry a premium price due to their enhanced properties and performance benefits, representing a significant portion of the float glass industry's value-added segment. An authoritative understanding of float glass pricing also involves recognizing environmental impacts. The industry faces increasing scrutiny over carbon emissions, prompting manufacturers to adopt sustainable practices. As eco-friendly production methods become prevalent, initial costs may rise; however, in the long-term, these practices offer cost savings through improved energy efficiency and resource management. Trust in float glass suppliers, therefore, hinges on their commitment to both innovation and sustainability, influencing purchasing decisions and pricing trends. Advisors recommend monitoring market publications and engaging in continuous dialogue with suppliers to navigate the intricate landscape of float glass pricing effectively. By investing in long-term partnerships and understanding supplier capabilities, buyers can secure favorable pricing while ensuring the quality and consistency of float glass products. In conclusion, the price trajectory of float glass is an intricate tapestry woven from production costs, market demand, regional influences, technological advancements, and environmental considerations. Navigating these factors requires a combination of experience, expertise, authority, and trustworthiness—qualities that professionals in the float glass market continually refine to understand and predict industry trends.
Next:
Latest news
-
Wired Glass: A Strong and Secure Glass Solution for Various Applications
NewsNov.04,2024
-
Tinted Glass: A Stylish and Functional Choice for Modern Homes
NewsNov.04,2024
-
The Elegance and Versatility of Silver Mirrors
NewsNov.04,2024
-
The Advantages of Copper Free Mirrors
NewsNov.04,2024
-
Tempered Glass: A Reliable Choice for Modern Applications
NewsNov.04,2024
-
Pattern Glass: Stylish and Functional Glass for Modern Design
NewsNov.04,2024
Related PRODUCTS