1 月 . 15, 2025 09:14 Back to list
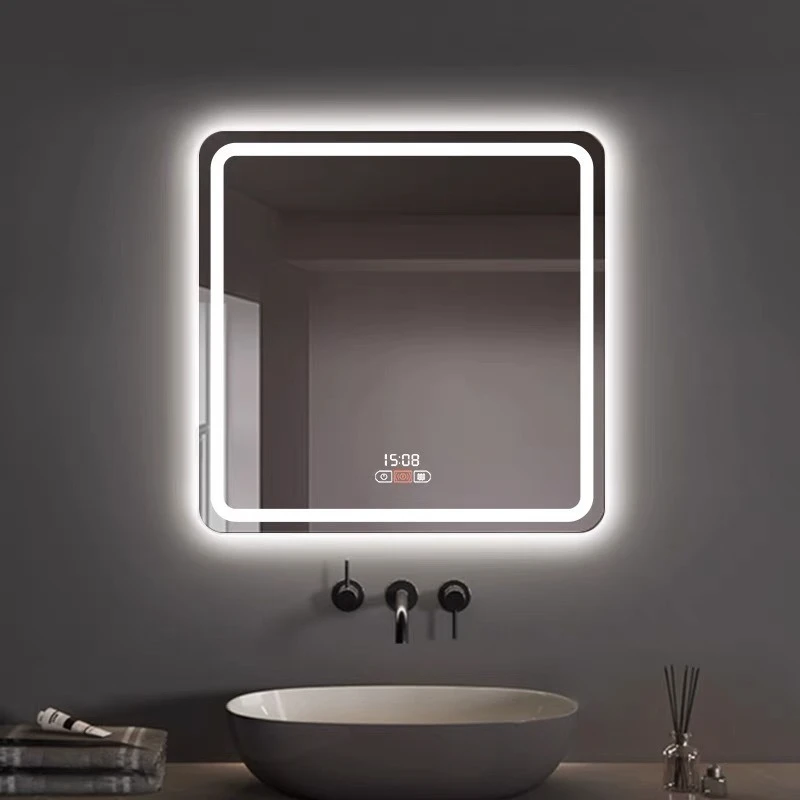
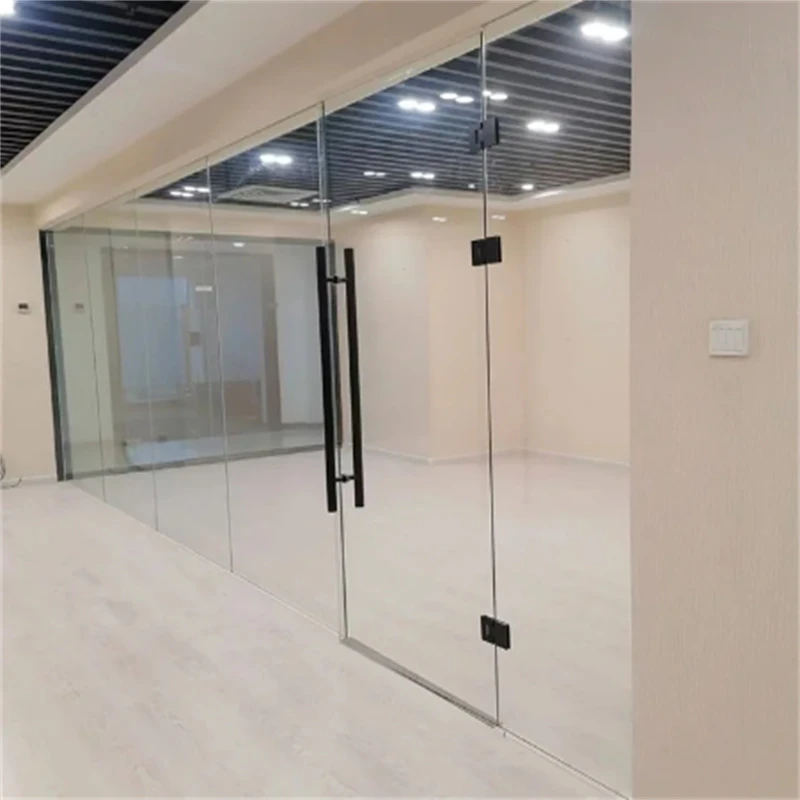
Float Glass
Cutting float glass is an intricate process that demands both technical finesse and a comprehensive understanding of the material's properties. As the backbone of modern architecture and various industrial applications, float glass is prized for its uniform thickness, transparency, and smooth surface. This flat glass is manufactured by floating molten glass on a bed of molten tin, hence the name float glass. The cutting process must preserve these attributes while achieving precision and minimizing waste.
Another authoritative practice involves annealing, a post-cutting treatment that alleviates internal stresses in the glass. Proper annealing enhances the durability and longevity of the glass product. Trust is built with clients through this careful attention to post-production details, demonstrating a comprehensive understanding of material science. The Role of Sustainability In cutting float glass, modern practitioners are increasingly focusing on sustainability. Efficient cutting methods aim to reduce waste, an essential consideration given the environmental impact of industrial glass production. By optimizing the layout during the cutting process, glass manufacturers can maximize raw material usage and minimize offcuts. Recycling initiatives further align with sustainable practices. Excess glass from cutting operations can be repurposed or recycled, ensuring that minimal material ends up in landfills. Establishing a recycling protocol not only enhances a company's sustainability credentials but also reflects an authoritative commitment to responsible manufacturing. Conclusion Mastering the art of cutting float glass encompasses a blend of advanced technology, environment control, safety measures, and sustainability practices. By adhering to these principles, companies position themselves as leaders in the industry, offering products that meet the highest standards of quality and precision. Through continuous innovation and dedication to sustainable solutions, they uphold their reputation for expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness. This well-rounded approach assures clients—whether in construction, automotive, or interior design industries—of receiving products that not only meet aesthetic and functional requirements but also align with global sustainability goals. In achieving this, the cutting of float glass isn't just a process; it's an exemplar of modern manufacturing excellence.
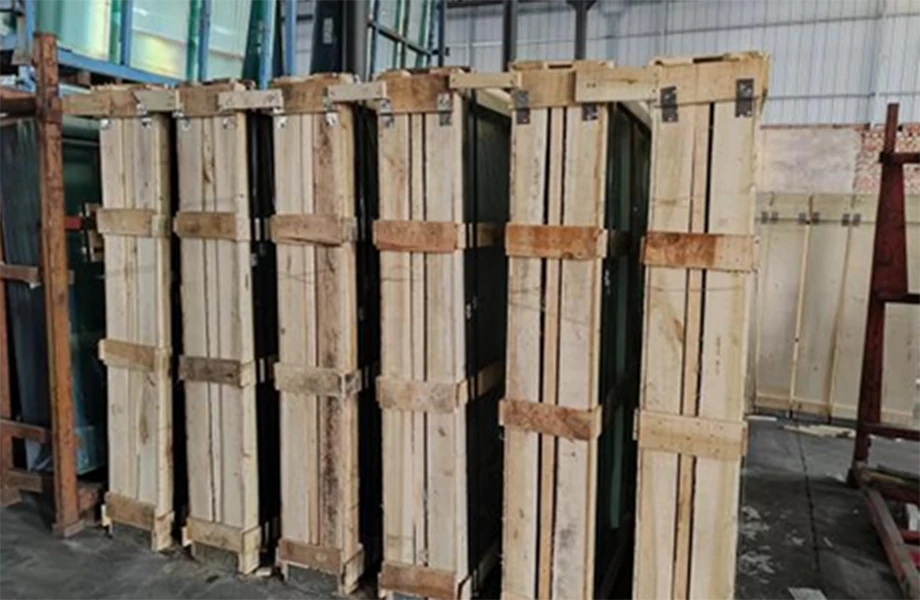


Another authoritative practice involves annealing, a post-cutting treatment that alleviates internal stresses in the glass. Proper annealing enhances the durability and longevity of the glass product. Trust is built with clients through this careful attention to post-production details, demonstrating a comprehensive understanding of material science. The Role of Sustainability In cutting float glass, modern practitioners are increasingly focusing on sustainability. Efficient cutting methods aim to reduce waste, an essential consideration given the environmental impact of industrial glass production. By optimizing the layout during the cutting process, glass manufacturers can maximize raw material usage and minimize offcuts. Recycling initiatives further align with sustainable practices. Excess glass from cutting operations can be repurposed or recycled, ensuring that minimal material ends up in landfills. Establishing a recycling protocol not only enhances a company's sustainability credentials but also reflects an authoritative commitment to responsible manufacturing. Conclusion Mastering the art of cutting float glass encompasses a blend of advanced technology, environment control, safety measures, and sustainability practices. By adhering to these principles, companies position themselves as leaders in the industry, offering products that meet the highest standards of quality and precision. Through continuous innovation and dedication to sustainable solutions, they uphold their reputation for expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness. This well-rounded approach assures clients—whether in construction, automotive, or interior design industries—of receiving products that not only meet aesthetic and functional requirements but also align with global sustainability goals. In achieving this, the cutting of float glass isn't just a process; it's an exemplar of modern manufacturing excellence.
Next:
Latest news
-
Wired Glass: A Strong and Secure Glass Solution for Various Applications
NewsNov.04,2024
-
Tinted Glass: A Stylish and Functional Choice for Modern Homes
NewsNov.04,2024
-
The Elegance and Versatility of Silver Mirrors
NewsNov.04,2024
-
The Advantages of Copper Free Mirrors
NewsNov.04,2024
-
Tempered Glass: A Reliable Choice for Modern Applications
NewsNov.04,2024
-
Pattern Glass: Stylish and Functional Glass for Modern Design
NewsNov.04,2024
Related PRODUCTS