1 月 . 20, 2025 04:38 Back to list
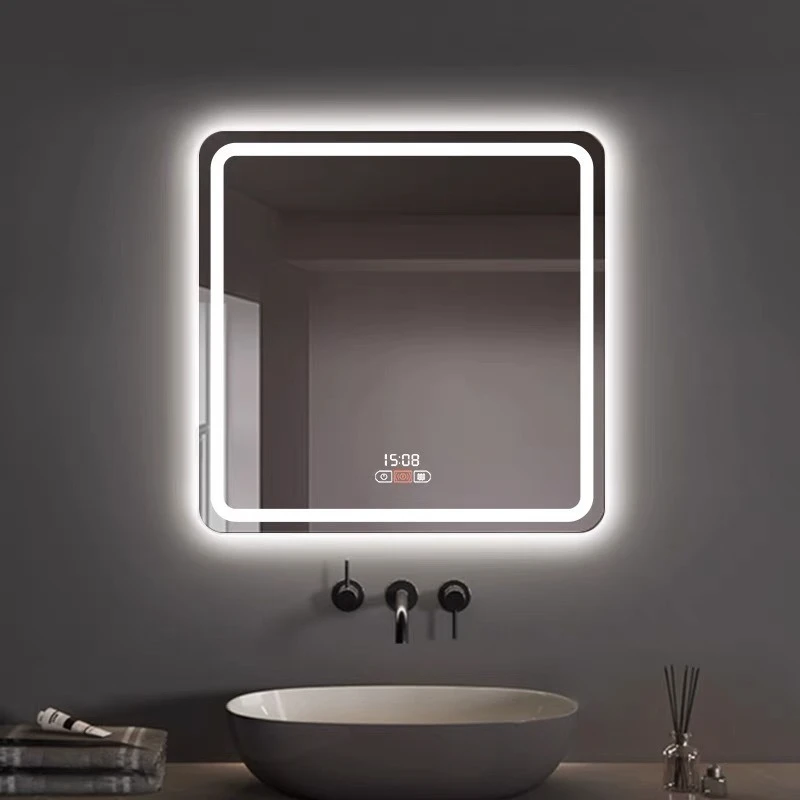
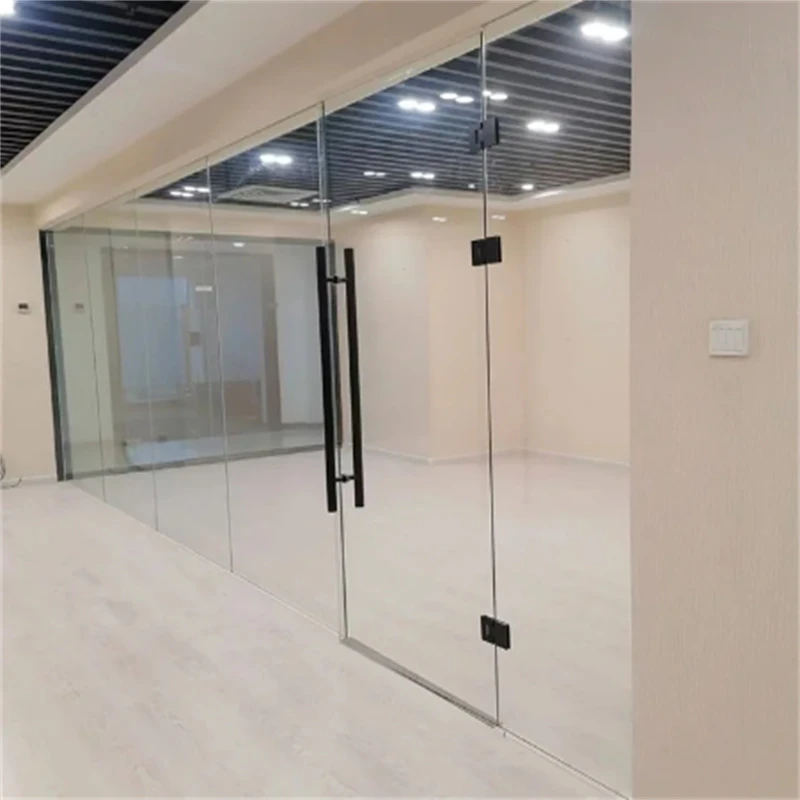
Coated Glass
Coated glass has emerged as a vital component in a multitude of industries, offering intriguing applications and solutions that extend beyond traditional uses. With advancements in technology, coated glass products bring innovative benefits that enhance product performance and user experience.
Another burgeoning application is in the solar energy sector, where anti-reflective and self-cleaning coated glass improves solar panel efficiency. By allowing more light to penetrate and reducing the dust accumulation, these coatings directly increase energy output from panels. In turn, this advancement supports the industry-wide push towards renewable energy solutions, affirming the importance of coated glass in the transition to cleaner energy sources. Healthcare settings also illustrate the innovative applications of coated glass. Antimicrobial coatings provide a layer of protection in environments that demand rigorous hygiene standards. These coatings help in significantly reducing the transmission of pathogens, making them indispensable in hospitals and clinics. With the increasing global awareness of hygiene and safety, the health sector's reliance on antimicrobial coated glass will likely expand, underscoring its trustworthiness in critical environments. In conclusion, the diverse and expanding applications of coated glass across various industries underscore its importance and flexibility as a modern material solution. By enhancing energy efficiency, safety, and durability, coated glass aids in achieving critical goals—from sustainability and cost-effectiveness to safety and hygiene. As industries continue prioritizing innovations that align with market needs and regulatory standards, the authoritative role of coated glass will only grow, making it an essential material for future technological advancements. This exemplifies not only the expertise embedded in the development of coated glass technologies but also the trust these innovations cultivate across industries.


Another burgeoning application is in the solar energy sector, where anti-reflective and self-cleaning coated glass improves solar panel efficiency. By allowing more light to penetrate and reducing the dust accumulation, these coatings directly increase energy output from panels. In turn, this advancement supports the industry-wide push towards renewable energy solutions, affirming the importance of coated glass in the transition to cleaner energy sources. Healthcare settings also illustrate the innovative applications of coated glass. Antimicrobial coatings provide a layer of protection in environments that demand rigorous hygiene standards. These coatings help in significantly reducing the transmission of pathogens, making them indispensable in hospitals and clinics. With the increasing global awareness of hygiene and safety, the health sector's reliance on antimicrobial coated glass will likely expand, underscoring its trustworthiness in critical environments. In conclusion, the diverse and expanding applications of coated glass across various industries underscore its importance and flexibility as a modern material solution. By enhancing energy efficiency, safety, and durability, coated glass aids in achieving critical goals—from sustainability and cost-effectiveness to safety and hygiene. As industries continue prioritizing innovations that align with market needs and regulatory standards, the authoritative role of coated glass will only grow, making it an essential material for future technological advancements. This exemplifies not only the expertise embedded in the development of coated glass technologies but also the trust these innovations cultivate across industries.
Next:
Latest news
-
Wired Glass: A Strong and Secure Glass Solution for Various Applications
NewsNov.04,2024
-
Tinted Glass: A Stylish and Functional Choice for Modern Homes
NewsNov.04,2024
-
The Elegance and Versatility of Silver Mirrors
NewsNov.04,2024
-
The Advantages of Copper Free Mirrors
NewsNov.04,2024
-
Tempered Glass: A Reliable Choice for Modern Applications
NewsNov.04,2024
-
Pattern Glass: Stylish and Functional Glass for Modern Design
NewsNov.04,2024
Related PRODUCTS